Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- tableau
- 아셈듀오
- 제네바경영대학교
- 태블로
- 교환학생주거
- 아셈듀오 선정
- 테이블계산
- 키워드시각화
- 제네바주거
- 제네바
- 패스트캠퍼스 #자료구조 #코딩테스트 #배열
- 태블로 포트폴리오
- 공모전후기
- 데이터 포트폴리오
- 미래에셋 공모전
- CRM
- 두잇알고리즘코딩테스트
- 교환학생
- 리뷰분석
- 텍스트분석 시각화
- 무신사 데이터분석
- MairaDB
- 교환학생 장학금
- 제네바기숙사
- 데이터공모전
- 파이썬
- 데이터 시각화 포트폴리오
- HEG
- 데이터 분석 포트폴리오
- 아셈듀오 후기
Archives
- Today
- Total
민듀키티
Microeconomic - Government Policies 본문
1. Price controls
(1) Price Ceiling vs Price Floor
- Price Ceiling (가격상한) : maximum on the price
- The price ceiling is binding if set below the equilibrium price -> leading shortage.
- Price Floor (가격하한) : minimum on the price
(2) Price Ceiling


- (a) A Price Celling That is not binding -> above the equilibrium price
- (b) A Price Celling That is binding -> below the equilibrium price -> leading shortage
- becase Demand quantitiy > Supply quantity
- nonprice rationing -> Long lines, discrimination by sellers


Example - The Price Ceiling on Gasoline
- the price celling is not binding and above the equilibrium price
- supply falls
- price celling becomes binding
- resulting in a shortage
- Case Study - Rent Control (임대료 통제)
- Gole of the rent control policy : to help the poor by making housing more affordable
- Short run : Supply and Demand both very inelastic ( 단기적으로, 임대주택의 수는 고정되어 있음. 즉 공급은 고정되어 있다. 집을 구하는 사람의 수는 변하지 않을 가능성이 높음. 즉, 단기적으로는 inelastic)
- Long run : Supply and Demand more elastic ( 장기적으로, 수요자와 공급자들이 민감하게 반응함. 공급자들은 (임대주택 주인들) 새로 짓지 않음. 수요자들은 임대주택을 구함. 즉, 장기적으로는 elastic


- Reasons of goverment intervene (이거 쫌 이해안감,, )
- No Perfect market competition : few landlords / many consumer
- heterogenous servie ,, ?? ,,
- Search and moving cost are high
- Imperfect competition : suboptimal allocation of resources, So goverment intervation could be efficeienct enhancing
- Equity issue
- Rich household more margin to adapt to changes in rents than poor household.
(3) Price Floor
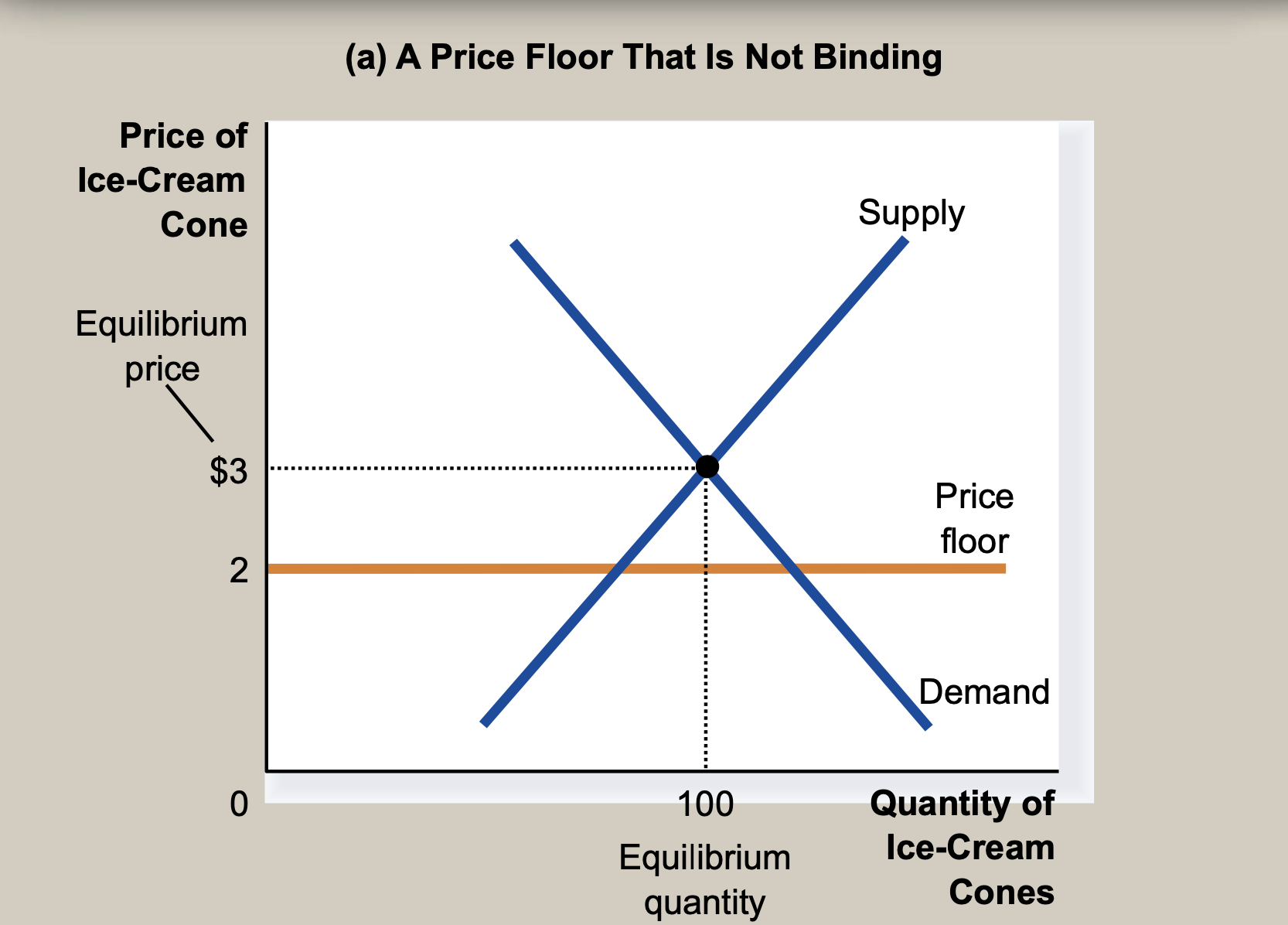

- (a) A Price Floor That is not binding -> below the equilibrium price
- (b) A Price Floor That is binding -> above the equilibrium price -> leading surplus
- becase Supply > Demand
- nonprice rationing -> The minimum wages ( important example of price floor ), agricultural price support
- Case Study - Minimum Wage
- Minimum Wage : Supply > Demand (즉, 공급량이 많다는 것은 실업이 발생하는 것을 의미)
- Minimum wages around the world


(4) Taxes
- Goal : to raise revenue for public projects
- Taxese discourage market activity
- Quantity sold is smaller
- Buyers and sellers share the tax burden
- Taxes result in a change in market equilibrium.
- Buyers pay more and seller receive less, regardless of whom the tax is levied on
- Case 1 : A Tax on buyers (소비자한테 부과하는 경우, 수요가 감소할 것임)
- A tax on buyers shifts the demand curve downward by the size of the tax ($0.5)
- Result : decrease quantity of ice - cream cones
- Price without tax : 3.00
- Price buyers pay : 3.30
- Price sellers recieve : 2.80
- Tax of buyers ( $0.3 ) > Tax of sellers ( $0.2 )

- Case 2 : A Tax on Seller ( 공급자에게 부과하는 경우, 비용이 증가할 것임)
- A tax on sellers shifts the supply curve upward by the amount of the tax
- Result : decrease quantity of ice - cream cones
- Price without tax : 3.00
- Price buyers pay : 3.30
- Price sellers recieve : 2.80
- Tax of buyers ( $0.3 ) > Tax of sellers ( $0.2 )

- Case 3 : A payroll Tax

(5) Elasticity and Tax Incidence
- How do the effects of taxes on sellers compare to those levied on buyers?


- (a) Elastic Supply, Inelastic Demand
- Scope : Supply < Demand
- Consumer tax > Producers Tax
- (b) Supply inelastic, elastic Demand
- Scope : Supply > Demand
- Conumer tax < Producers Tax
(6) The Costs of Taxation
- How do taxes affect the economic well-being of market participants? - Key Concept: The Deadweight loss of taxation

- (the goverment's) Tax Revenue : the size of the tax (T) * the quantity of good sold (Q)

- A deadweight loss is the fall in total surplus that results from a market distortion, such as a tax.
- Deadweight : C+E

(7) How a Tax Affects Market Participants
- The change in conusmer surplus
- The change in producer surplus
- The change in tax revenue
- The losses to buyers and sellers exceed the revenue raised by the goverment.
- The fall in total surplus is called the deadweight loss
(8) Determinations of the deadweight loss
- The greater the elasticities of demand and supply :
- the larger will be the decline in equilibrium quantity and
- the greater the deadweight loss of a tax




- (a) Inelastic Supply : the deadweight loss of a tax is small
- (b) elastic Supply : the deadweight loss of a tax is large
- (c) Inelastic Supply : the deadwieght loss of a tax is small
- (d) elastic Supply : the deadweight loss of a tax is large
(9) Deadweight loss and tax revenue as taxes vary
- After a specific interval, the tax revenue decreases
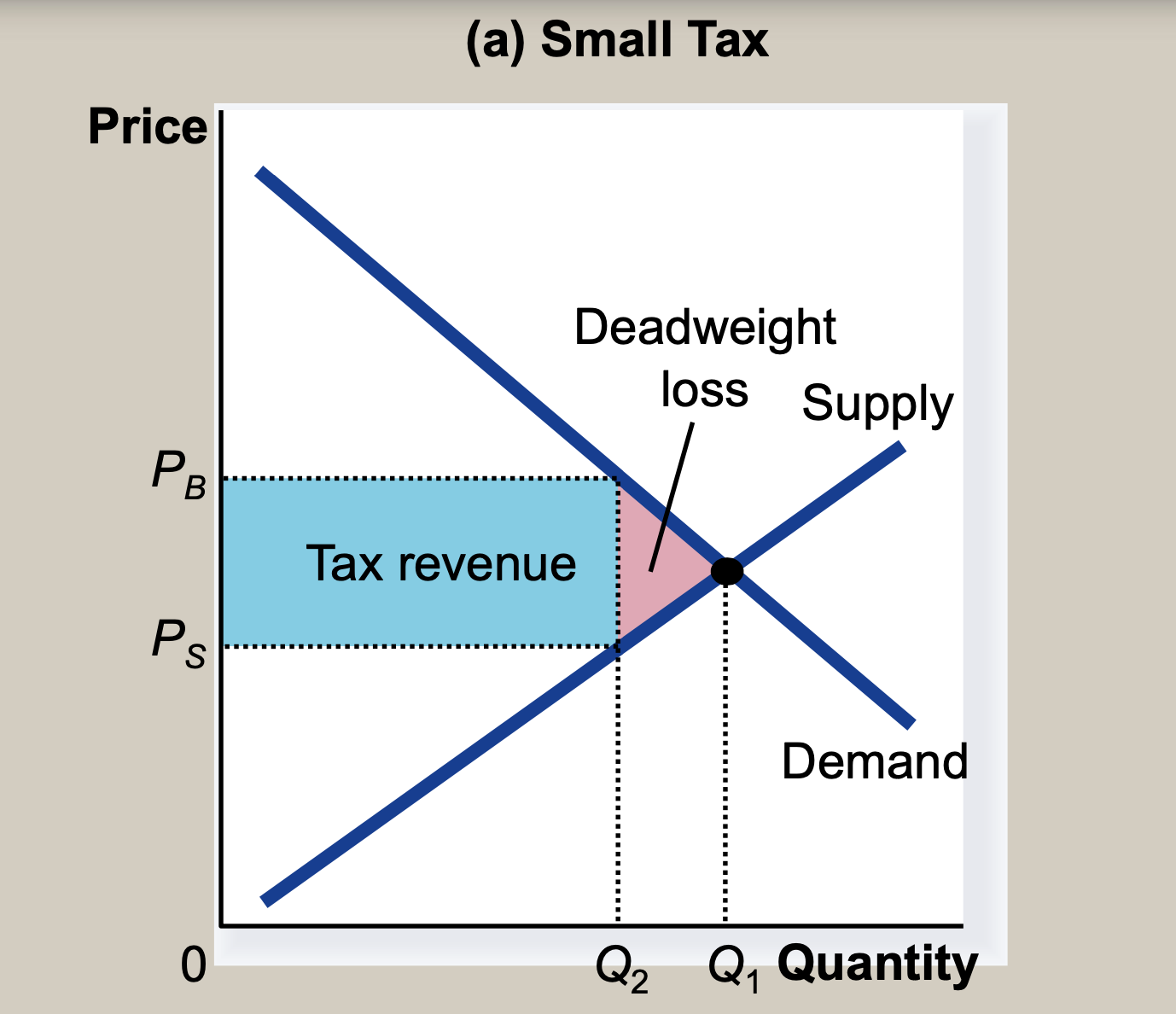
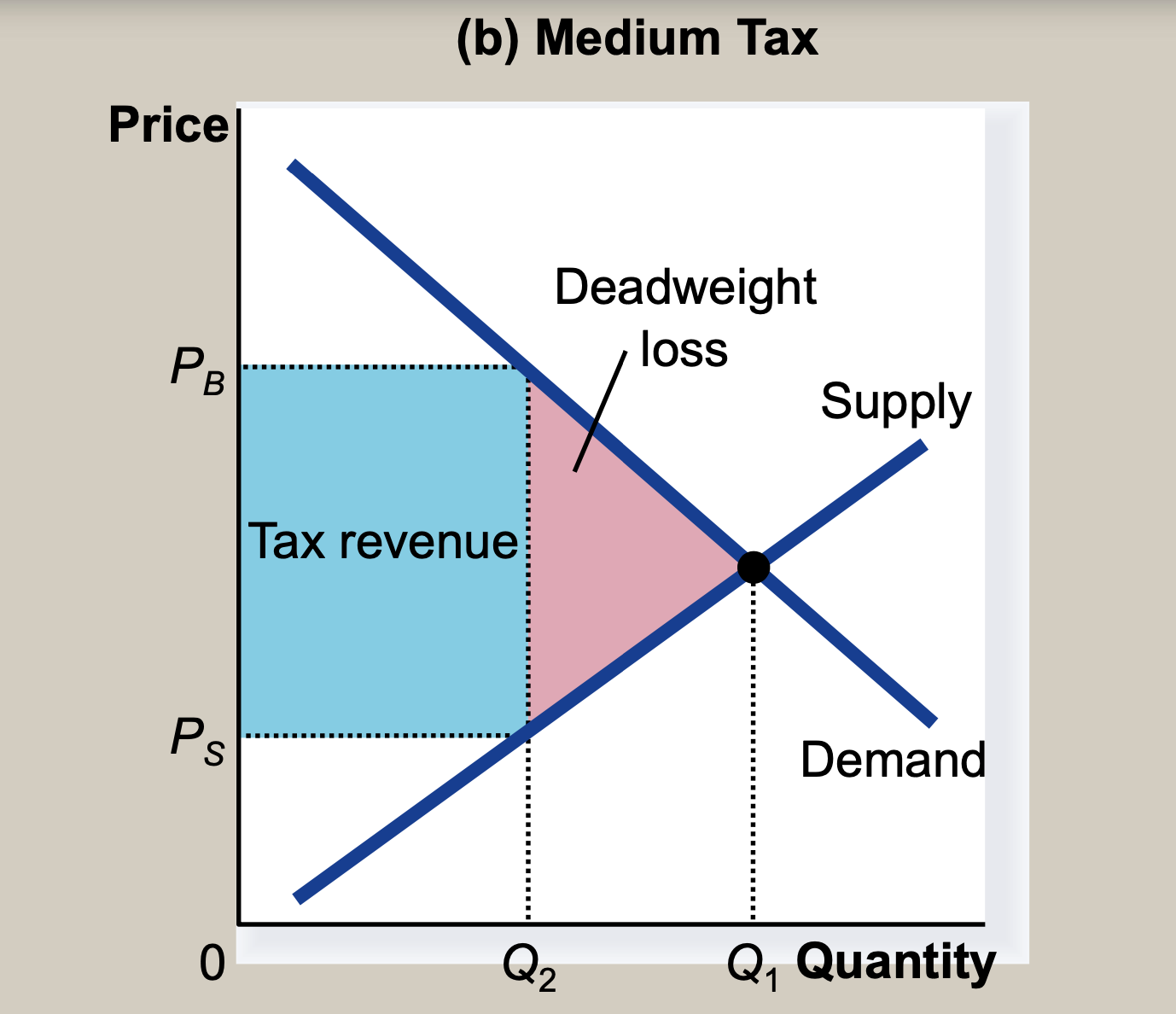
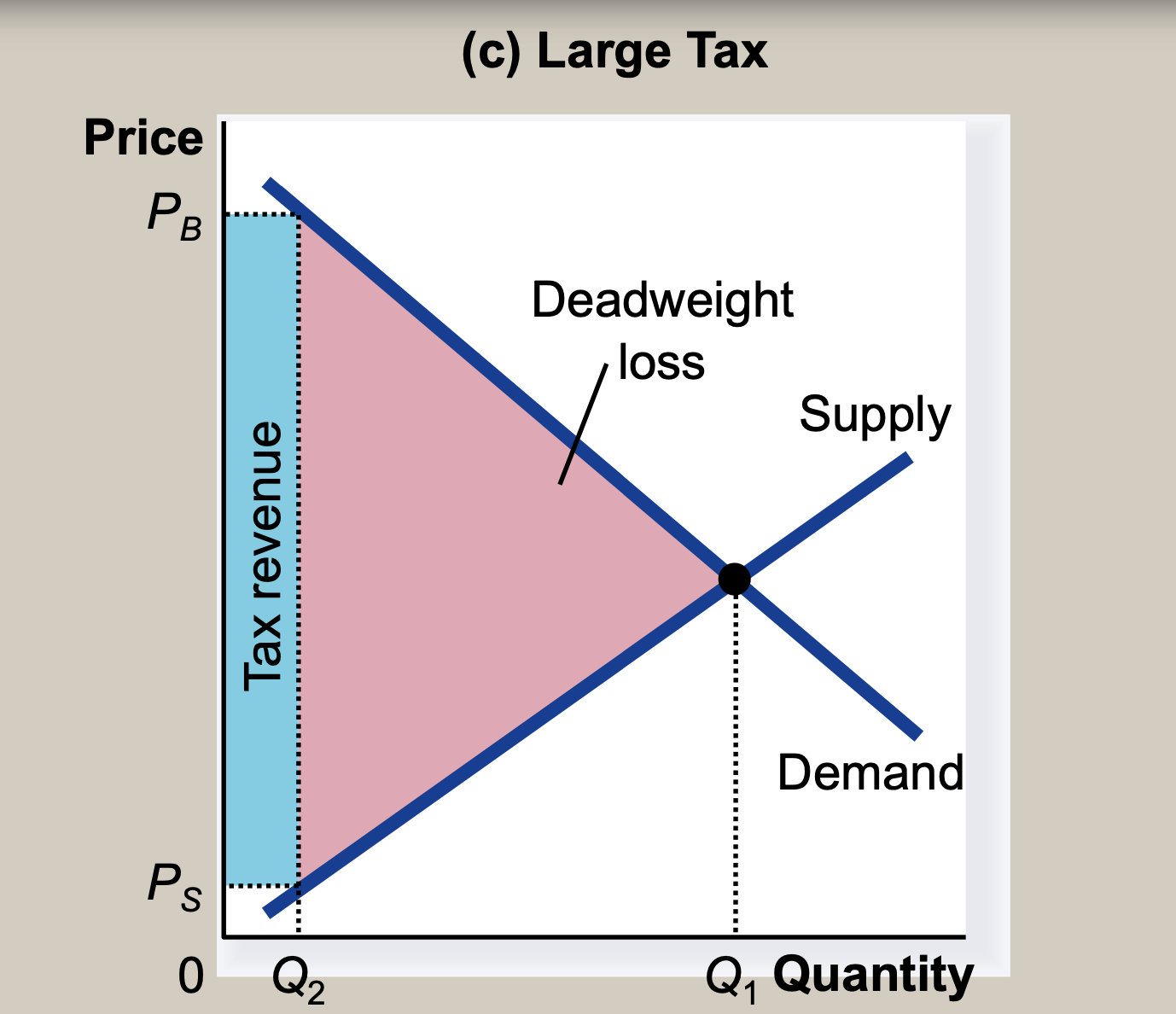
- As the size of a tax increases, its deadweight loss quickly gets larger.
- But,tax revenue first rises with the size of a tax, but then, as the tax gets larger, the market shrinks so much that tax revenue starts to fall
- So, Revnnue curve is same to Laffer curve (relationship between tax rates and tax revenue)


'International Businessment' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Microeconomics - Monopolies 1 (0) | 2023.12.20 |
|---|---|
| Microeconomic - Externalities (0) | 2023.12.19 |
| Microeconomics - Public Goods (0) | 2023.12.18 |
| Microeconomics - Elasticity and its Applications (0) | 2023.10.15 |
| Microeconomics - Supply and Demand (0) | 2023.10.15 |
