| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- 공모전후기
- 테이블계산
- tableau
- 리뷰분석
- 데이터공모전
- 데이터 시각화 포트폴리오
- 텍스트분석 시각화
- 교환학생주거
- 아셈듀오 선정
- 제네바
- 데이터 포트폴리오
- HEG
- 아셈듀오 후기
- MairaDB
- 데이터 분석 포트폴리오
- 제네바주거
- 키워드시각화
- 교환학생 장학금
- 태블로 포트폴리오
- 제네바기숙사
- 미래에셋 공모전
- CRM
- 무신사 데이터분석
- 제네바경영대학교
- 패스트캠퍼스 #자료구조 #코딩테스트 #배열
- 아셈듀오
- 두잇알고리즘코딩테스트
- 교환학생
- 태블로
- 파이썬
- Today
- Total
민듀키티
Microeconomics - Supply and Demand 본문
나는 여기와서 왜 미시경제학을 듣고있는가 ,,,,🥲
1. Organization of Economic Activity
(1) Three Problems All Economic Systems Must Address
- What should be produced? (ex. Establish production targets for factories and farms)
- How should it be produced? (ex. Plan how to achieve the goals)
- For whom will it be produced? (ex. Distribute the goods and services produced)
(2) Free-Market or Capitalist Economic System
- Which careers to pursue
- Which products to produce or buy
- When to start and shut-down a business
- Who gets what is decided by individual preferences and purchasing power
2. Market Economies
- Modern microeconomics : supply, demand, market equilibrium (시장균형)
- market : a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service
- buyers determin demand
- sellers determin supply
3. Types of Markets
- competitive market : has a negligible impact on the market price
- Products are the same
- many buyer & many saller
- Buyers and Sellers are price takers
- Monopoly : one seller / seller controls price
- Oligopoly : Few sellers
- Mononpolistic Competition : Many seller / Slightly differentiated products / Each seller set price for its own product
4. Introduction to Demand
Quantity demand : the amount of a good that buyers are willing and able to purchase
- Law of Demand : other things equal, when the price of the good rises, the quantitiy demanded of a good falls
- Demand Schedule : relationship between the price of the good and the quantity demanded

- decrease in price -> increase quantity of cones demanded
- Demand Curve : graph of relationship between the price of good and the quantity demad
5. Market Demand vs Individual Demand
- Market demand : sum of all individual demands for a particular good or service (glaph also)

When price of ice - cream cones is 2.00, Catherine's demand is 4 and Nicolas's demand is 3
So, Market demand is 7 (4+3) = all buyer
6. Change in Quantity Demanded vs Shifts in the Demand Curve
(1) Changes in Quantity Demanded
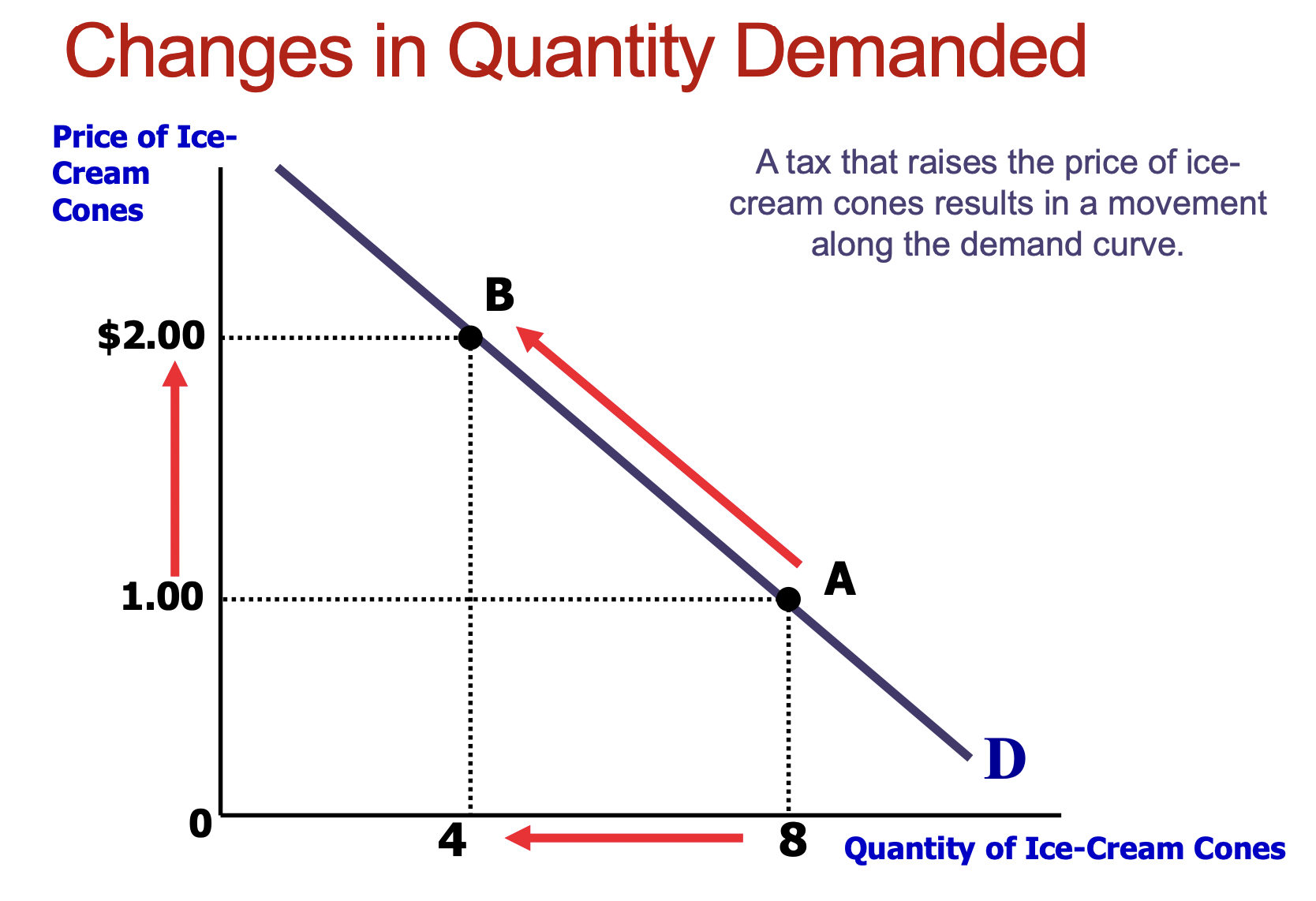
A tax that raises the price of icecream cones results in a movement along the demand curve.

- Shift right : Increase in Demand
- Shift left : Decrease in Demand
- Variabels that can shift the demand curve : Income, Prices of related goods, Tastes, Expectations, Number of buyers
(2) Shifts in the Demand
- Normal good : Other thing constant, increase in income leads to increase in demand
- Inferior good : Other thing constat, increase in income leads to decrease in demand
So, Normal good vs Inferior good


Left picture is Normal good (Shift rigth) , and Right picture is Inferior good (Left side)
7. Shifts in the Demand
- Prices of related goods
- Substitutes : An increase in the price of one -> Leads to an increase in the demand for the other
- Complements : An increase in the price of one -> Leads to a decrease in the demand for the other
- Tastes
- Expectations about the future
- Number of buyers
(1) Shift in the Demand Curve vs Movement along the Demand Curve

- Shift the demand curve : Public service announcements, Mandatory health warnings on cigarette packages, Prohibition of cigaretted advertising on tv
- Movement along demand curve : Try to raise the price of cigrattes
- Graph (a) : warnging on cigarette packages -> demand curve shift to left (from D1 to D2) -> quantity demand falls from from 20 to 10
- Graph (b) : tax rises the price of cigrattes -> demand curve does not shift, instead, movement demand curve -> price rises from 2.00 to 4.00 -> quantitiy demand falls from 20 to 12
8. Inroduction to Supply
(1) Term
- Quantity supplied : Amount of a good sellers are willing and able to sell
- Law of supply : Other things equl, when the price of the good rises, quantity supplied of a good rises
- Individual supply : Supplt of one seller
- Supply Schedule and Supply Curve

- Supply Schedule : table that shows the quantitiy supplied at each price
- Supply Curve : graphs that supply schedule
(2) Market Supply
It is same the sum of individual supplies

(3) Change in Quantity Supplied vs Shifts in the Supply Curve
- Change in quantitiy supplied

- Shifts in the Supply Curve

- Any change that raises the quantity that sellers wish to produce at any given price shifts the supply curve to the right.
- Any change that lowers the quantity that sellers wish to produce at any given price shifts the supply curve to the left.
- Input price, Technology, Expectations about future, Number of sellers
9. Equilibrium. : Supply and Demadn Together
(1) Equilibrium
- Suply and demand forces are in balance
- Quantity supplied = Quantity demanded
- Supply and demand curves intersect
(2) Equilibrium price / Equilibrium quantity
- Balances quantity supplied and quantity demanded

- Surplus : Quantity supplied > quantity demandee
- Downward pressure on price
- Movement along the demand and supply curves
- Increase in quantity demanded
- Decrease in quantity supplied
- Shortage : Quantity demanded > quantity supplied
- Upward pressure on pirce
- Movement along the demand and supply curves
- Decrease in quantity demanded
- Increase in quantity supplied

10. Changes in Equilibrium

----
Problem sets A
1. You were planning to spend Wednesday evening working at your part-time job. but a friend asks you to attend a show of your favourite singer Lady Gaga at the Geneva which tickets costs
- The total cost of attending Lady Gaga's show includes its momentoy cost (150 CHF)
- oopportunity cost (time etc)
2.
a. How does this change affect the incentives for working ?
- Incentives are about marginal changes in costs or benefits motivating people to respond.
This reform of the goverment will increase the welfare fund. whcih is generally collected in the form of taxes by working people. It will increase the cost of working, decrease their incentive to work.
b. between equilty and efficency
- trade -off
- increase equity (redistribution)
- low efficency ( continue to not work, quantitly produce less)
3. Positive vs Negative
4. Micro vs Macro
-----
Problem Sets B
1. Demand and Supply function
Qp = 4000 - 3p
Qs = 800 + 5p
(1) 4000 - 3p = 800 + 5p (방정식)
p = 400
(2)
price 400. Quantity 2800
(3) At a price CHF 300, is there a surplus or a shortage in the market for electirc heaters, and by how much ?
Qp = 4000 - 3*300 = 3100
Qs = 800 + 5 * 300 = 2300
there is shortage 800 (3100 - 2300)
(4) Suppose there is a significant increas in global temperatures, reducing the need for heading
- An increase in global temperature will reduce the need for heating, affecting consumer' willingness by buy electirc heaters. The demand curve will then be affected
- The demand curve shifts to the left leading to decrease in both the equilbrium price and quantity
- Demand curve move to left
2. what opportunity cost of producing 1 ton of apples for Sophie and for Luca ?
Sophie = 7 (140 / 20)
Luca = 0.33 (30 / 90)
---
강조한 내용들
'International Businessment' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Microeconomics - Monopolies 1 (0) | 2023.12.20 |
|---|---|
| Microeconomic - Externalities (0) | 2023.12.19 |
| Microeconomics - Public Goods (0) | 2023.12.18 |
| Microeconomic - Government Policies (1) | 2023.12.18 |
| Microeconomics - Elasticity and its Applications (0) | 2023.10.15 |
